
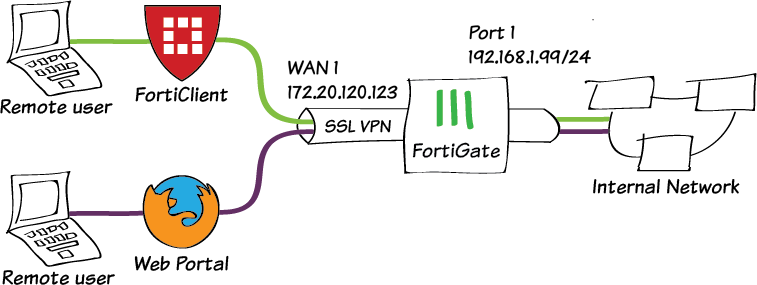

The feature comprises of an SSL daemon running on the FortiGate unit, and a web portal, which provides users with access to network services and resources including HTTP/HTTPS, Telnet, FTP, SMB/CIFS, VNC, RDP, and SSH. Support for SSL VPN web-only mode is built into FortiOS. Web-only mode offers true clientless network access using any web browser that has built-in SSL encryption and the Sun Java Runtime Environment (note that there is no minimum Java/JRE version requirement-any version of Java/JRE currently supported by the supplier of the Java/JRE for the operating system should work). Web-only mode provides remote users with a fast and efficient way to access server applications from any thin client computer equipped with a web browser. The user group settings specify whether the connection will operate in web-only mode or tunnel mode. A successful login determines the access rights of remote users according to user group. When a remote client connects to the FortiGate unit, the FortiGate unit authenticates the user based on username, password, and authentication domain. Any data sent back is first encrypted, and is decrypted when it reaches the client.įortiOS supports the SSL and TLS versions defined below: When the information reaches its destination, it is decrypted using a secret (private) key. Once the successful connection is established, the browser encrypts all the information before it leaves the computer. SSL protection is initiated automatically when a user (client) connects to a web server that is SSL-enabled. SSL establishes an encrypted link, ensuring that all data passed between the web server and the browser remains private and secure. SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) as HTTPS is supported by most web browsers for exchanging sensitive information securely between a web server and a client. In most areas, access to the Internet is readily obtainable without any special arrangements or long wait times. Perhaps more important though is the universal availability of the Internet. Rather than utilizing expensive leased lines or other infrastructure, you use the relatively inexpensive, high-bandwidth Internet. The advantages of a VPN over an actual physical private network are two-fold. A VPN tunnel is a non-application oriented tunnel that allows the users and networks to exchange a wide range of traffic regardless of application or protocol. When data is encoded and transmitted over the Internet, the data is said to be sent through a “VPN tunnel”. VPNs also ensure that the data transmitted between computers cannot be intercepted by unauthorized users. VPNs use encryption and other security methods to ensure that only authorized users can access the network. A VPN is a secure logical network created from physically separate networks. SSL is not strictly a Virtual Private Network (VPN) technology that allows clients to connect to remote networks in a secure way. Information is encapsulated at Levels 6 – 7 (Presentation and Application layers), and SSL VPNs communicate at the highest levels in the OSI model. SSL VPNs establish connectivity using SSL, which functions at Levels 4 – 5 (Transport and Session layers).
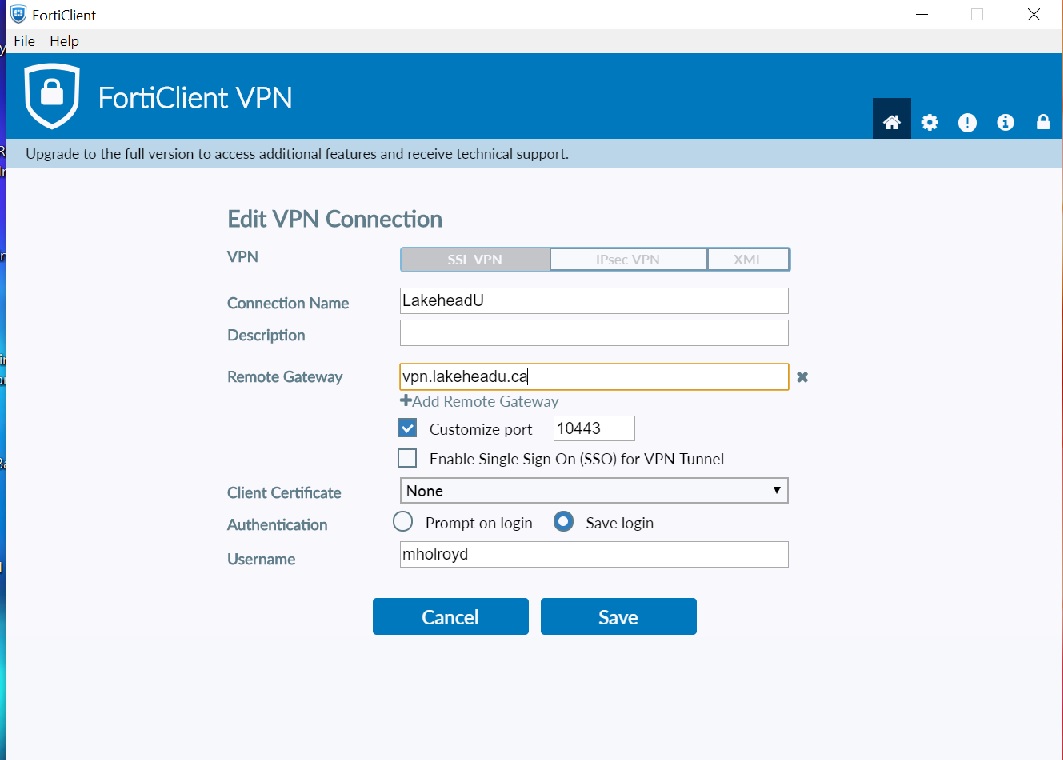
As a result of the growing need for providing remote/mobile clients with easy, cost-effective and secure access to a multitude of resources, the concept of a Virtual Private Network (VPN) was developed. Employees traveling across the country or around the world require timely and comprehensive access to network resources. In addition, businesses are expected to provide clients with efficient, convenient services including knowledge bases and customer portals. As organizations have grown and become more complex, secure remote access to network resources has become critical for day-to-day operations.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
